What can differentiation look like in the classroom?

The aim of differentiation is to maximise the potential of every learner and to ensure incremental growth and a sense of achievement. Teachers select and sequence appropriate teaching and learning to engage and support all students.
This section looks at the practical application of differentiation in the classroom.
Teachers effectively differentiate by:
-
ensuring teaching, learning and assessment is planned around the syllabus with clear, shared learning intentions and success criteria
-
using the appropriate data and information available to inform planning
-
using flexible learning environments and grouping which is responsive to student needs
-
altering the pace and manner of delivery in response to immediate and reflective student feedback
-
selecting and modifying resources in response to student needs and learning goals
-
setting appropriate learning goals according to student needs and readiness
-
focusing on high intellectual quality and significance
-
making high expectations explicit for all student learning (Teaching AC English website).
Quality Teaching model
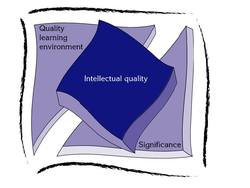
The NSW Quality Teaching model is a research-based framework. It underpins the policies, programs, syllabuses, guidelines and continuums provided by NSW Department of Education and Communities educators to support quality education.
This model of pedagogy addresses three core dimensions:
-
Intellectual quality
-
Quality learning environment
-
Significance.
The elements within each dimension show teaching opportunities available to incorporate differentiation strategies for all students.
Further information is available at Quality Teaching resources. In particular, Quality teaching in NSW public schools – A classroom practice guide includes elements that are important for differentiation. The Quality teaching in NSW public schools - Coding scale overview provides a tool for teacher self-assessment and reflection.
There are many correlations between the Quality Teaching model and Tomlinson’s elements. Explore these connections in the next tab, Four elements.
Elements to differentiate
Tomlinson (2004) encourages teachers to focus on four elements of differentiation:
What teachers teach and how students gain access to that body of knowledge.
Content is the knowledge, skills, understandings that we want students to learn. The differentiation of content focuses on how students will acquire this information so that all students gain access to knowledge and build on their existing knowledge. (Intellectual quality and Significance)
Strategies include:
-
providing various ways for students to access content, knowledge and skills
-
presenting information through various modes of delivery
-
using concrete materials for some learners and abstract concepts for other learners.
How a student understands the information, ideas and skills at the heart of a lesson.
Process is how students learn. It ensures that students make meaning of information, ideas and skills in a lesson. (Quality learning environment)
Strategies include:
-
tiered activities which provide different levels of support, challenge and complexity
-
using interest centred activities
-
implementing flexible time intervals for achieving outcomes
-
providing additional support for learners who experience difficulty and encouraging fast learners to deepen their knowledge of topics and broaden their learning by progressing further.
Demonstrations of what students know, understand and can do following an extended sequence of learning.
Product refers to the demonstration of what students have come to know, understand and be able to do as the result of an extended sequence of learning. (Intellectual quality and Significance)
Strategies include:
-
student choice in how they demonstrate their learning
-
encouraging students to express their learning in various ways
-
providing a variety of task products with explicit quality criteria known to the student
-
scaffolding tasks to provide an appropriate level of challenge for each student.
The operation and tone of a classroom.
Learning environment includes classroom organisation, design and atmosphere to optimise student learning. (Quality learning environment)
Strategies include:
-
encouraging various styles of learning in the classroom through set up, organisation and flexible grouping
-
setting guidelines for independent learners.
|
|
Activity 4: Linking Quality Teaching model and differentiation elements There are many correlations between the Quality Teaching model and Tomlinson’s four elements. Work collaboratively within your school or team to demonstrate your shared understanding of the correlation between the Quality Teaching model and Tomlinson’s four elements. Complete this activity using either the table in the Activity booklet or by uploading and sharing this activity template (.docx 35kB) through an online collaboration tool such as Microsoft Office 365 or Google Apps. |
This activity is an opportunity to use the DEC’s collaboration tools. In preparing for the activity, the presenter will need to upload and share the online document with participants before the session. Detailed instructions for each platform are included below:
Practical ideas and support for differentiation

There is considerable support material for teachers to access as they differentiate content, process, product and learning environment.
The Differentiation toolbox presentation explores some practical strategies that teachers use to cater for student diversity when planning for differentiation.
Additional materials
-
8ways – Aboriginal ways of learning
-
EAL/D Teacher Resource Australian Curriculum
-
Differentiation strategies for language learners (.docx 41kB)
-
SCAMPER model – Powerhouse Museum
Differentiated teaching ideas developed by NSW Public Schools
The following sample teaching strategies K-10 were produced by NSW Public Schools as part of the 2013 Differentiated Curriculum Learning Project. Within these samples you will see explicit inclusion of differentiation for content, process, product and learning environment.
|
Primary |
||
|
Secondary |
||
|
|
‘TEN Hits the Target at Casino Public School’ is a DEC ClassMovies video that showcases differentiation applied to Process and Learning environment with the Targeted Early Numeracy program. |
|
|
Activity 5: Unit of learning modification plan Identify opportunities where differentiation of content, process, product and learning environment could be incorporated into your unit of learning. You may choose strategies from the Differentiation in practice tab to plan for modifications. Consider the questions in the Activity booklet to guide your planning. |


