The Geography K–10 Syllabus provides detailed continuums which show a progression of concepts, skills, tools, and knowledge and understanding from Early Stage 1 through to Stage 5. These concepts, skills and tools illustrate the increasingly complex development of knowledge and understanding through engagement in the geographical inquiry process.
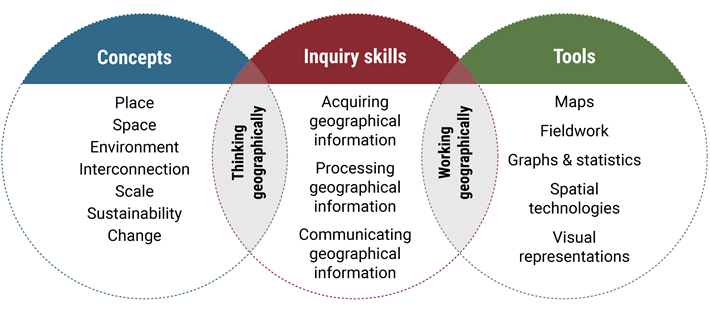
The diagram below represents the interconnection of the continuums of learning and how these in turn support ‘thinking geographically’ and ‘working geographically’. This diagram is based on a model developed by Stuart Delandre (Principal, Illawarra EEC).
|
|
Watch or listen to What is geography for? by Malcolm McInerney, Chairperson AGTA. |

© G Braiding
Geographical concepts provide a lens through which geographical phenomena and issues are investigated. These are the key ideas supporting students to think geographically. The key concepts outlined in the syllabus are integral to geographical understanding.
Examine the syllabus descriptions of the seven geographical concepts: place, space, environment, interconnection, scale, sustainability, change.
The following core geographical questions can be used to identify how the concepts assist students with geographical understanding:
What is where? Think: place, space, environment, scale
Why there? Think: interconnections, change, environment
Why care? Think: sustainability
|
|
Read about the core concepts of place, environment and space in the article What is geography? |
Review the geographical concepts continuum from the Geography K–10 Syllabus, focusing on one stage that you select as well as the previous and next stages.
|
|
Activity 3: Geographical concepts Develop a diagram or flowchart in your Activity booklet that displays the connections between the seven key geographical concepts. |
Geography inquiry skills enable geographers to think geographically and work geographically at the same time.
|
|
Examine the K–10 geographical inquiry skills continuum from the Geography K–10 Syllabus. |
|
|
 © A Southwell Activity 4: Geographical inquiry skills Access the K–10 geographical inquiry skills continuum on pages 3–4 of the K–10 geography continuum document (.pdf). You may wish to download and/or print it. Use one colour to highlight the geographical nouns and another to highlight the geographical verbs in the skills descriptions for the stage you have selected. It is ideal to colour code across several stages to see the skills progression. When completing the course in a small group, this could be achieved by colleagues addressing different stages. How could you use this information to develop the use of geographical skills with your students? Record your response in your Activity booklet. |
Geographical tools are about working geographically.
|
|
View the presentation Geographical tools (.ppsx 4MB), which looks at the multidisciplinary tools used to collect and process geographical data and information. |
|
|
 Activity 5: Geographical tools checklist Complete the geographical tools checklist in your Activity booklet. Referencing your selected stage, discuss/reflect on how to confidently use the listed geographical tools. Describe how you can develop your use of geographical tools, particularly in the area of spatial technologies. Activity 6: Geographical tools continuum Access the K–10 geographical tools continuum on pages 5–6 of the K–10 geography continuum document (.pdf). You may want to download and/or print it. For your selected stage, identify one geographical tool you would like to know more about. Undertake a short investigation about the use of this tool and record the information in your Activity booklet. Share your understanding with colleagues. |
Learning across the curriculum content areas of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures, Asia and Australia’s engagement with Asia, sustainability, and civics and citizenship are included in the academic discipline of geography as specific syllabus subject matter. Sustainability is also described as a geographical concept. The active citizenship component of civics and citizenship is often the outcome of a geographical inquiry.
|
|
View the presentation Learning across the curriculum (.ppsx 2MB). |

© G Braiding
Embedded geographical content
Select one of the following learning across the curriculum content areas. Read and then reflect on or discuss how specific geographical learning content supports this area.
-
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures
-
Asia and Australia’s engagement with Asia
-
Sustainability
-
Civics and citizenship
|
|
Use the BOSTES filter content tool to search a stage(s) of the geography syllabus for one or more of the above areas. Note the interconnections between these areas in the syllabus content. Consider:
|
|
|
Activity 7: Embedded learning across the curriculum content Refer to one focus area for your chosen stage and select a content description with a variety of learning across the curriculum content icons. Brainstorm and record teaching and learning ideas to support the learning across the curriculum content within this content description. Select one further learning across the curriculum content area that aligns with a school priority. Examine this area in more detail using both the description and the filter tool available on the BOSTES website. Consider:
|

© A Southwell
What do geographers do?
Geographers study where things are and how they got there.
Geographers seek to understand why the world is the way that it is, and to participate in shaping sustainable futures. Geographers investigate the character of places, the distribution of phenomena across space, biophysical processes and features, and dynamic relationships between humans and environments.
Sourced from Institute of Australian Geographers, FAQ
|
|
View the presentation Syllabus content (.ppsx 3MB). |
The Organisation of content diagram from the Geography K–10 Syllabus shows the central role that the geographical concepts, skills and tools play in developing students’ knowledge and understanding.
The syllabus Table of objectives and outcomes — continuum of learning demonstrates how the outcomes progress the development of both knowledge and understanding, and geographical inquiry skills.
|
|
Activity 8: Continuum of learning Access the ‘continuum of learning’ table linked above and complete the following:
In your Activity booklet, record your findings with reference to the implications for the stage you have selected. |




