Overview
Electricity – what is it?
Why is this girl’s hair standing up? Static electricity was the first kind of electricity that people discovered. We can all produce it by stroking a cat or rubbing a balloon. Electricity can do useful work – if you use the correct device you can get heat, light, motion or other forms of energy from electricity. Survey a classroom or a room in your house and find the electrical appliances. You could make a list like the one below.
Hairdryers convert from electricity into... What devices do you know that convert other forms of energy into electricity? You could make a list, using the table above as a starting point.
Use the Sources tab to investigate some sources of electricity and think about how we might keep using electricity in the future. |
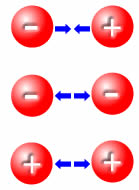
Static versus current
A Van der Graaff generator looks like an aluminium ball on top of a perspex column. It creates hair-raising effects. Benjamin Franklin’s kite – truth or myth? You decide. Either way, don’t try it at home! Ben Franklin's kite - truth or myth? If you take off a jumper on a dry windy day you’ll sometimes hear a crackling noise. This noise is caused by miniature lightning strikes! The attraction between negative and positive particles gets so great that electrons jump from one place to another. When electrons move like this, they are not static any more – they form a current. If the girl in the picture pushed her hair together, it would spring apart again. We spend energy pushing the hair together. While the hair is held together the energy is stored and we get it back as it springs apart. The usual way for us to move electrons is through a metal wire. Most metals are good conductors of electricity – they allow the electrons to move through easily.
|
||||||||||||||||||||